Biometric Authentication on iOS and Android: A full Guide
Biometric Authentication on iOS and Android: A full Guide
But how do you add biometric authentication functionality to your mobile app? And does this functionality make sense for your business? Why is biometric authentication so integral to a seamless app user experience? In this article, we go deep with answering these questions. But to save you some time, here's a small cheatsheet of today’s talking points:
- What is biometric authentication as it relates to mobile devices?
Biometric authentication capabilities provide a secure means to verify the identity of users on mobile devices by scanning biometric data like fingerprints, retinas, and face structures.
- Why are biometrics like Face ID and Touch ID important/popular with users and app developers alike?
Biometrics offer app users a secure and hassle-free alternative to manually entering passwords or codes. App developers also favor biometrics as it enhances customer engagement by eliminating this major hurdle.
- What kinds of businesses use biometrics as part of their mobile app experience?
A wide range of businesses and industries that prioritize privacy and security, such as the banking and healthcare sectors, have adopted biometric authentication in their mobile app experiences.
- What is Apple Face ID / Touch ID?
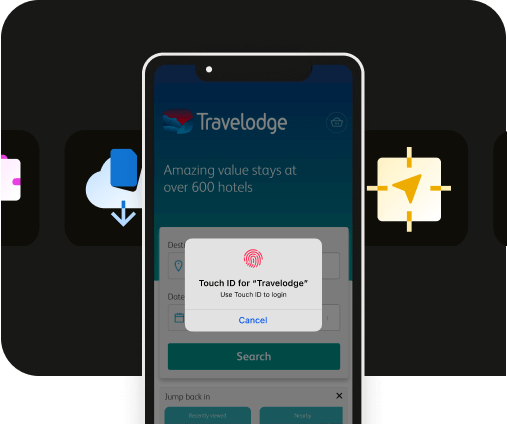
Both Face ID and Touch ID are powerful authentication techniques employed on iPhones. Touch ID scans the user's fingerprint once it is placed on the sensor, comparing it to the stored fingerprint data for authentication. In the case of Face ID, the technology projects an intricate pattern of infrared dots on the user's face, capturing and analyzing the unique facial features. Tip: See Apple’s developer overview for more information.
- What is Android Biometrics?
Android Biometrics refers to a range of sensors available on Android devices that can scan various biometric data, including fingerprints, retinas, and facial structures. These sensors enable users to authenticate themselves securely, providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive information stored within mobile apps. Android offers both strong and weak biometric features as a trade-off between usability and security, allowing you to customize the authentication experience based on your app's requirements and user expectations (see Android developer guides for more detail).
Need a deeper dive on biometric authentication in Android and iOS apps? Keep reading!
What is Biometric Authentication as it relates to mobile devices?
Biometric authentication capabilities provide a secure means of verifying a user’s identity on their mobile devices.
The term "biometrics" in this context encompasses Android Biometrics as well as Apple’s Touch ID and Face ID. Biometrics is a range of sensors — such as fingerprint reader, retina scanner, face Scanner, or camera — that (as the names suggest) scan biometric data like fingerprints, retinas, and face structures to authenticate users.
Why is Biometric Authentication and Face ID / Touch ID popular with users and app developers alike?
Biometrics have gained immense popularity among users due to their convenience, speed, and enhanced security. With biometrics, users no longer need to remember and input complex passwords or codes, making the authentication process quick and hassle-free.
Moreover, biometric authentication is generally considered highly secure, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information. App developers also favor biometrics as it enhances customer engagement by eliminating the major hurdle of logging in with lengthy email and password combinations.
What kinds of businesses use biometrics as part of their mobile app experience? 2 use cases
A wide range of businesses and industries prioritize privacy and security, leading them to adopt biometric authentication in their mobile app experiences.
Biometrics Use Case #1: Finance
One prominent industry that extensively utilizes biometrics is the banking sector. Banks understand the importance of secure access to financial information and have integrated biometric functionality into their mobile apps. For instance, major financial institutions in the US, such as American Express and Bank of America, offer biometric authentication options to their customers.
Biometrics Use Case #2: Healthcare
Another category of businesses that leverage biometrics in their apps is the healthcare industry, where protecting sensitive patient data is crucial. Imprivata, for instance, has integrated its OneSign solution with Microsoft Azure, allowing its healthcare clients to access their data on the cloud using biometric screening of fingerprints as an identification method.
Apple Face ID / Touch ID vs. Android Biometrics: What are they, and what's the difference?
The good news is that biometric authentication functionality is available for both iOS and Android users. Let’s see in more detail how this functionality works on each platform.
What is Apple Face ID / Touch ID?
Both Face ID and Touch ID are powerful authentication techniques employed in iPhone-based apps. Apple's Touch ID is a proprietary technology developed by Apple that allows users to scan their fingerprints on a mobile device. It provides a convenient and secure way for users to authenticate their identity and then unlock their iOS devices.
On the other hand, Apple’s Face ID is a more advanced authentication technology introduced by Apple. It utilizes infrared-based 3D face scanning technology that creates a detailed map of a user’s face, and securely authenticates their identity. With Face ID, your iPhone can recognize you even in low-light conditions or when you're wearing glasses, a hat, or a mask (see Apple developer overview for more detail).
How does Apple Face ID / Touch ID work?
Touch ID scans the user's fingerprint once it is placed on the sensor, comparing it to the stored fingerprint data for authentication. In the case of Face ID, the technology projects an intricate pattern of infrared dots on the user's face, capturing and analyzing the unique facial features. This data is then converted into a digital fingerprint, which is compared to the stored fingerprint for authentication.
In most Apple devices, a dedicated security chip, known as the T2 chip, handles biometric authentication. Recent iPhones and M1 Macs incorporate the biometric authentication functionalities directly into the main System on Chip (SoC).
What devices support iPhone Face/Touch ID?
Touch ID has been around since 2013, and is now available on iPhones 5S and newer models, as well as 2017 and newer models of MacBooks. On the other hand, Face ID is a feature exclusive to iPhone X and newer models.
What is Android Biometrics?
‘Android Biometrics’ refers to a range of sensors available on Android devices that can scan various biometric data, including fingerprints, retinas, and facial structures. These sensors enable users to authenticate themselves securely, providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive information stored within mobile apps (see Android developer guides for more detail).
How does Android Biometrics work?
Similar to Apple's approach, Android Biometrics scans and stores digital fingerprints or other biometric data to authenticate users. When a user initiates the biometric authentication process, the sensor captures the relevant biometric information, compares it to the stored data, and determines whether the user is authenticated.
Depending on the device and sensor type, Android Biometrics may also utilize dedicated hardware components for enhanced security. These components ensure that the biometric data is securely stored and processed within the device, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
What devices support Android Biometrics?
Android, being a vast ecosystem, encompasses many devices that support biometric authentication. Most modern Android smartphones and tablets come equipped with some form of biometric sensor, allowing users to leverage the convenience and security of biometric authentication. Note that different device manufacturers market Android Biometrics differently. On their Pixel devices Google refers to Face Unlock and Fingerprint Unlock. On their Galaxy devices Samsung refers to Facial recognition and Fingerprint recognition.
Sidebar: what are strong vs. weak Biometrics?
Recently, Median released an update that provides support for Android weak biometrics. It's essential to understand the distinction between strong and weak biometrics to make informed decisions regarding the security and usability of your app.
Strong biometrics incorporate dedicated biometric hardware, such as fingerprint scanners or infrared facial scanners, to verify the user's identity. These biometric methods offer an extremely low false- positive chance and are considered highly secure and difficult to fool.
On the other hand, weak biometrics rely on less secure hardware, such as camera-based face scanners or retina scanners. While these methods still provide an additional layer of security, they may have a somewhat higher false- positive chance compared to strong biometrics. Additionally, weak biometrics may have limited usability in certain conditions, such as face scanners in dark environments.
It's up to you as the developer to specify the minimum level of biometrics to accept in your app. This decision determines the trade-off between usability and security, allowing you to customize the authentication experience based on your app's requirements and user expectations.
For more information, read: Median Documentation - Android Biometrics
How do I add Android Biometric and Face ID / Touch ID functionality to my webview app?
If you have a mobile web app or a webview app (app built by converting a website into an app) and you want to incorporate biometric authentication, Median's Biometric Authentication Native Plugin for Android offers a simple and efficient solution. This plugin enables you to add full-feature biometrics to your webview app without the need for native development.
To add biometric authentication functionality to your mobile webview app, follow these easy steps:
- Get the plugin. Add the premium module to your app from the App Builder, and use the Median JavaScript Bridge commands provided in our documentation for each of the following steps to access its functionality.
- Check for the presence and availability of biometric capabilities. If biometrics are available, then the status check will also indicate the presence of a previously saved secret. If there are no biometric capabilities available, a biometric login dialog should not be displayed to the end user.
- Save the secret on successful login. Once a user has successfully logged, in you may save a secret to the device that can be used to login again in the future. On iOS, Median uses the iOS Keychain technology, which in turn leverages cryptographic hardware, to ensure that the secret cannot be retrieved without biometrics from the user. On Android, Median uses the Android Keystore, which in turn leverages on-device cryptographic hardware, to ensure that the secret cannot be retrieved without biometric authentication from the user.
- Retrieve the secret. The next time the user needs to log in to your website, and the status check indicates a secret is available, the website should attempt to retrieve the secret from the device.
- Authenticate the user’s biometrics. At this point, the user will be shown a dialog prompting them to authenticate via biometrics. If the biometrics are provided successfully, the secret will be released by the on device cryptographic hardware and returned via a promise or JavaScript callback. If biometrics are unsuccessful, an error will be returned.
What other plugins support user authentication?
In addition to biometric authentication, we offer other plugins and services that support user authentication in your mobile app. Two notable examples are Social Login and Auth0:
- Social Login: This plugin allows users to sign in to your app using their existing social media accounts, such as Facebook and Google. This plugin simplifies the authentication process and improves user experience by eliminating the need to create new accounts or remember additional credentials. Social Login also supports biometrics on iOS, specifically with "Sign in with Apple," offering an additional authentication option for Apple device users.
- Auth0: This is an authentication and authorization platform that provides comprehensive solutions for user authentication in mobile apps. It offers a wide range of authentication methods, including traditional username and password, social login, and multi-factor authentication. Auth0 supports biometrics on both iOS and Android, empowering developers to incorporate biometric authentication seamlessly into their apps.
Enter the new era of authentication with Median’s Biometric Authentication plugin
So, there you have it! Biometric authentication is truly changing the game when it comes to securing our mobile apps. Gone are the days of relying on pesky codes and passwords that are easily forgotten or compromised.
With biometric authentication, you can provide your app users with a seamless and convenient experience, all while ensuring top-notch security.
If you're itching to give your app’s login functionality a modern authentication makeover, look no further than our plugin library. We've got a selection of cutting-edge authentication methods, including biometric authentication, just waiting for you to explore.
And, if you need help don’t stress, we can help: our expert team can advise on what’s needed to integrate native plugins within your app.

to top